Environment
Situation
Machines that run a Linux kernel not shipped by the vendor for distributions listed above are not supported by the supplied versions of the blkwatch module. However, it is possible to recompile the blkwatch module for systems that are running any of the supported distributions with a non-standard kernel (user-built or debug). To use the blkwatch module with such kernels, it must be recompiled for the specific (source workload) kernel and incorporated back into the PlateSpin product.
Resolution
On the PlateSpin server, navigate to the Platespin application's installation directory, as applicable to the environment:
C:\Program Files\PlateSpin Migrate Server
C:\Program Files\PlateSpin Protect Server
D:\Program Files\PlateSpin Forge Server
1. Open the '.\Packages\9D470BFF-E30F-4015-83D8-4D308A8C8B1B' folder and copy the file named '1.package' (or '2.package', if using Forge 3.3 HotFix 2 or Protect 10.3 HotFix 2) out to a temp directory.
2. Rename 1.package file with .zip extension (1.zip). Extract the contents of 1.zip file to this temporary folder.
3. Use ssh / Winscp or a usb key to copy the 'src' subfolder to the Linux machine that is capable of building modules for the specific kernel. To build modules for a specific kernel, it is required that both a kernel development package (kernel-devel for RHEL or kernel-source for SLES) for the corresponding target kernel and a gcc compiler be installed on the linux machine. If those are missing, please install them before moving forward.
4. Navigate to the 'src' directory on the Linux machine and run the following command:
'make'
This will produce a 'blkwatch.ko' file in the 'src' directory.
5. Run the following command to get the release string of the kernel:
'uname -r'
6. Go back to the PlateSpin server and create a subfolder in the temporary folder where the package file was extracted (as in step 2). Create a new subfolder for this customer driver using the following naming convention:
CustomKernel-<release string>-<architecture>
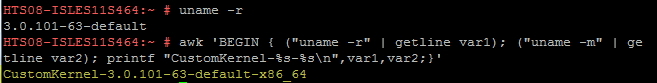
Or you may run the below command to get durectly the full name for the folder. See illustration as an example:
awk 'BEGIN { ("uname -r" | getline var1); ("uname -m" | getline var2); printf "CustomKernel-%s-%s\n",var1,var2;}'2.6.32.54-0.3.el6.x86_64
In that case the folder name will look like this:
CustomKernel-2.6.32.54-0.3.el6.x86_64-x86_64
7. Copy the blkwatch.ko produced in step 4 to the subfolder created in step 6.
8. Compress the contents of temporary folder (see note below in bold) using the .ZIP target format. Make sure that the compressed file contains all the folders that were extracted in step 2, in addition to the new one created in step 6. Rename the new archive to '1.package' (replace .zip extension with .package).
***Make sure to only archive the contents within the temp folder, NOT the temporary folder itself. If the folder is archived it will create an additional layer in the package, causing no block-based components to be found***
Additional Information
make[1]: Entering directory `/usr/src/kernels/2.6.18-308.el5-x86_64'
make[1]: Entering directory `/usr/src/redhat/SOURCES/linux-2.6.18.4'
If kernel-devel (RedHat) or kernel-source (SLES) is not installed, install it. Both this package and gcc are required to properly build blkwatch.ko files. If this package is not installed, or not installed for the correct kernel version, the build will fail or the blkwatch.ko file will not be correct.